1. Traditional and digital dentistry
Traditional
Traditional
At present, most of the production methods of dental prosthesis in the world are the continuation of the traditional manual manufacturing method. First, the doctor prepares the restored patient’s tooth, and then uses the impression material to extract the negative model and reproduce the plaster model. Then professional technicians complete complex processes such as applying gap agent, cutting, and engraving wax-up. After embedding and casting into a metal restoration, the baked restoration is evenly on a porcelain furnace, and finally they will finish the restoration.
Therefore, most dental hospitals have a huge technical center responsible for the processing and production of patient restorations. For dental clinics, they will choose to cooperate with a professional dental laboratory. The main work of the dental laboratory is to make corresponding restorations after receiving the plaster tooth model sent by the dental clinic.
However, it is clear that the above manufacturing steps all require manual operation by a craftsman. The efficiency is low, the precision is not high, and the treatment cycle is very long, which cannot meet the needs of patients to quickly restore tooth function.
Digital
Digital
Therefore, a new technology for the rapid manufacture of dental restorations based on CAD/CAM came into being, also known as digital dental restoration. It introduces the powerful functions of computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing into the manufacture of dental prostheses.
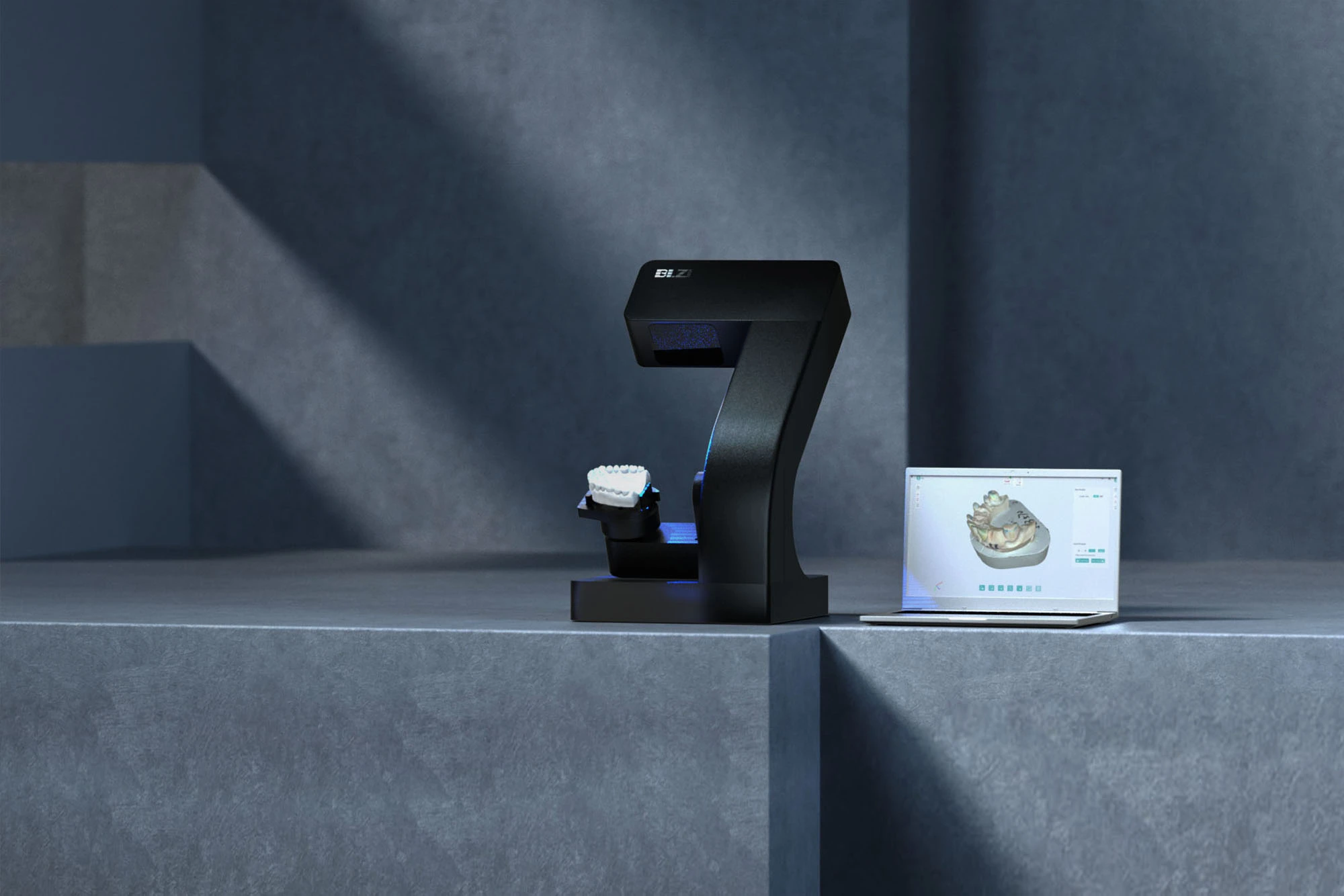
The dental clinic can use the intraoral scanner to directly obtain the patient’s intraoral digital model, and directly send the digital model file to the dental laboratory. Or a dental lab could receive a plaster model from the clinic and use a lab scanner to convert the model into a digital file itself.
Next, you only need to import the file into the design software, you can design, and then choose to use the milling machine, 3D printer and other equipment to directly make the restoration. This changes the traditional treatment time measured in weeks and months into hours and minutes, which significantly shortens the treatment cycle, improves work efficiency, relieves the pain of patients, and improves the accuracy and quality of the restoration.
Patients only need 30 to 60 minutes of treatment to quickly complete the oral restoration of various diseased teeth and restore the function of the oral and jaw system. Digital prosthodontics has a profound impact on the theory and practice of prosthodontics, and its popularization and application is a technological revolution in modern prosthodontics.
Above all, truly dental laboratory scanners worth adding, which might help a lot.
2. Digital dental workflow
Computer Aided Design/Computer Aided ManufacturingCAD/CAM has been in a stage of continuous development and improvement since it was introduced into the field of dental prosthesis in the 1970s. As a CAD/CAM system for oral restoration, it usually consists of three parts: the acquisition of oral shape information; the design of computer-aided restorations (CAD); and the fabrication of computer-aided restorations (CAM).
Among them, the first part is the acquisition of three-dimensional data information about the oral cavity, that is, measuring and extracting the shape of the oral cavity by various measurement methods, and then obtaining the three-dimensional data model of the oral cavity shape by using three-dimensional reconstruction technology. Scanners are inseparable from relationships. The second part is to use the computer-aided technology to design the restoration of this data model (computer model), and obtain the required data information of the restoration. The last part is to use CAM to process the data information of the restoration.
3. Why do you need dental laboratory scanner?
1、Free publicity
For a long time, stomatology is an image science based on the evaluation of visual effects and manual operations. Its development is mainly based on experience accumulation and summarization. The shape and structure of the human oral cavity is a complex system. Experience and image to guide the clinical, it is far from enough.
It is necessary to find out the numerical regularity of its existence in order to grasp the problem more comprehensively and deeply. Therefore, the digital engineering of stomatology is not only the inherent requirement of its own development, but also the mainstream direction of future medical development.
Having a lab scanner means your lab goes digital. Through this behavior, you can improve the grade and level of your laboratory, and a different laboratory means more advanced technology. This is a free publicity that brings more clients to the lab.
2、Save working time
No matter domestically or internationally, the conventional production methods of traditional oral fixed restorations are mainly metal precision casting or precision casting and then porcelain, etc., which must be individually produced by hand, which is cumbersome in processing technology, low in production efficiency, and requires a lot of working time. long.
Even if the potential of traditional casting technology is fully exploited, it can only partially improve the traditional dental prosthesis manufacturing process, and cannot fundamentally solve the problem.
Having a lab scanner means you can do more in less time. Originally, only 10 restorations could be made a day, but now 100 can be done a day due to the addition of laboratory scanners (of course, this is just a metaphor). The increase in efficiency directly brings about an increase in overall revenue.
3、Traditional clinic friendly
The benefits of dental laboratory scanners are manifold. Obviously, when the digitalization of dentistry has not yet completed and matured, most dental clinics still use traditional impressions and molds to make plaster tooth models. This is a process that must be experienced in a revolution, and no one can avoid it.
In the face of such a situation, the dental laboratory must respond. The laboratory scanner can help it cooperate with the dental clinic, process the plaster model faster, and convert it into a digital file to still meet the digital needs of the dental laboratory.